radon measurement, radon gas, Home inspection, continuous radon monitor
What is Radon?
Radon is a colorless, odorless, radioactive gas. It forms naturally from the decay of radioactive elements, such as uranium, which are found in different amounts in the ground throughout our state and the world. Radon moves through the ground into the air and water. Radon is everywhere. It is at a normally low level in the outdoor air and the water in streams and rivers. Much higher levels are found in some homes and underground water sources.
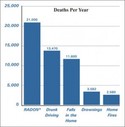
Radon is a serious health issue that causes 21,000 deaths each year and is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. The number of deaths caused by radon is 6 times the number attributed to carbon monoxide poisoning and house fires combined.
The cost of a radon test is a small price to pay to ensure the safety of your family. You should test for radon every two years.
Radon is a serious health issue that causes 21,000 deaths each year and is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. The number of deaths caused by radon is 6 times the number attributed to carbon monoxide poisoning and house fires combined.
The cost of a radon test is a small price to pay to ensure the safety of your family. You should test for radon every two years.
How does Radon enter your home?
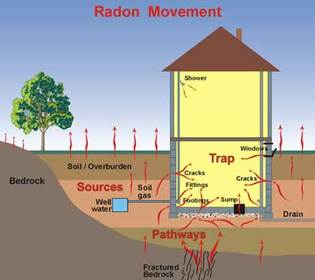
Radon can enter a house through any opening. The gas can be at high levels whether or not it is built on a slab or crawlspace. It passes through cracks in the slab and if the home has a crawlspace, the gas seeps through gaps in the framing. Two houses could be within feet of one another and one could have a high level and the other could have a low level of radon. The only way to be sure of the amount of radon in the home is to have it tested.
Newer homes are more air-tight than older homes. That is great for energy efficiency but can lead to higher radon levels because the air cannot escape.
Seasonal changes and the weather can impact radon levels. Heavy rain can increase levels by simply pushing down on the gas, leaving the home as the only place for radon to escape. High winds and snow have similar effects.
Newer homes are more air-tight than older homes. That is great for energy efficiency but can lead to higher radon levels because the air cannot escape.
Seasonal changes and the weather can impact radon levels. Heavy rain can increase levels by simply pushing down on the gas, leaving the home as the only place for radon to escape. High winds and snow have similar effects.
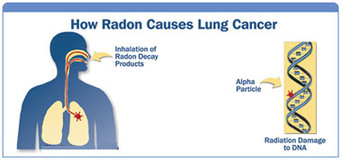
How it gets in your body.
|
Radon gas breaks down into solid radioactive particles called radon progeny. Radon progeny attaches to dust in the home and can be taken into our lungs when we breathe in these areas. As these particles break down, they emit radiation that can damage the DNA inside your cells. The EPA recommends any home with a reading of 4 or higher should be mitigated.
|
Continuous Radon Monitor CRM
I use a continuous radon monitor to measure the amount of radon gas in the structure. It is placed in the lowest living area.
|
Visit North Carolinas' radon page here.
|
|
Click here to watch a video on the discovery of radon as well as its impact on our lives.
(video is about 45 minutes long) |